- Accueil
- A Propos
- Expertises
-
-
Numerique
-
Distribution
-
-
- Contact
- Blog
- +33 6 69 51 05 20
- Prendre RDV
- Accueil
- A Propos
- Expertises
-
-
Numerique
-
Distribution
-
-
- Contact
- Blog
- +33 6 69 51 05 20
- Prendre RDV
Le règlement européen sur la résilience opérationnelle numérique du secteur financier, aussi dit « règlement DORA » (Digital Operational Resilience Act), est une initiative de l’Union européenne visant à renforcer la résilience numérique des acteurs du secteur financier.
Avec l’augmentation des cybermenaces et des attaques ciblant les infrastructures critiques, DORA impose des obligations strictes pour assurer la sécurité des systèmes d’information et garantir la continuité des services essentiels.
DORA est entrée en application le 16 janvier 2023, mais les entités concernées disposent d’une période de transition jusqu’au 17 janvier 2025 pour se conformer pleinement à ses exigences. Cette période vise à permettre aux entreprises de revoir leurs politiques internes, de mettre à jour leurs contrats, et de s’assurer que toutes les mesures nécessaires à la conformité sont en place.
DORA ne se limite pas à un simple cadre légal : elle établit des normes qui affectent non seulement les institutions financières, mais également leurs prestataires de services technologies de l’information et de la communication (TIC).
Ainsi, les entreprises concernées doivent non seulement se conformer aux exigences techniques, mais également s’assurer que leurs contrats, pratiques internes, et politiques de sécurité respectent ces nouvelles normes.
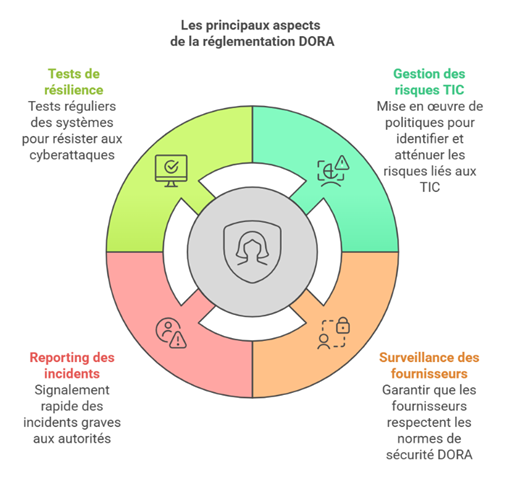
La réglementation DORA vise à garantir que les acteurs du secteur financier, ainsi que leurs prestataires de services TIC, peuvent prévenir, résister et se rétablir rapidement face à des incidents informatiques. Ce cadre repose sur plusieurs piliers essentiels qui imposent des obligations spécifiques :
Un accompagnement juridique spécialisé peut aider à analyser en détail chacune de ces exigences et à assurer une conformité optimale avec le règlement DORA.
La mise en conformité avec la réglementation DORA nécessite une approche structurée. Un avocat peut vous guider à travers les étapes suivantes :
Toutefois, la conformité avec la réglementation DORA ne se limite pas à une mise en œuvre initiale : elle nécessite un suivi continu et des ajustements réguliers pour rester en phase avec les exigences. Cela implique plusieurs actions essentielles.
Tout d’abord, il est nécessaire d’analyser les évolutions réglementaires, car la réglementation DORA peut être modifiée ou précisée par des actes délégués, comme les RTS (Regulatory Technical Standards). Un avocat s’assure que votre entreprise demeure à jour sur ces changements.
Ensuite, la mise en place d’un plan de suivi est cruciale pour intégrer des contrôles réguliers visant à garantir la conformité des processus, des politiques et des contrats.
Enfin, il convient de se préparer aux audits externes, ce qui implique d’organiser les documents requis et de structurer efficacement les réponses aux questions des régulateurs.
Conseils pratiques pour réussir les évaluations de conformité :
Avantages de l’accompagnement juridique pour la conformité à DORA :
Se conformer à la réglementation DORA est une étape cruciale pour protéger votre entreprise contre les cybermenaces et garantir la résilience de vos opérations numériques. Cependant, cette conformité peut être complexe et nécessiter des compétences spécifiques. Faire appel à un avocat présente plusieurs avantages :
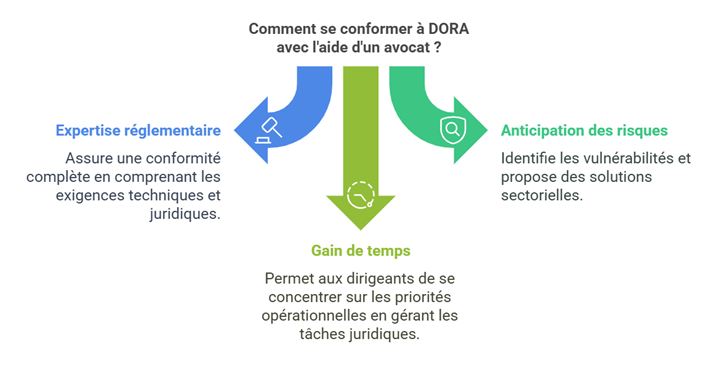
La réglementation DORA concerne des domaines techniques et juridiques pointus, notamment la cybersécurité et la gestion des risques TIC. Un avocat formé en réglementation financière et numérique comprend les enjeux spécifiques du secteur financier et peut adapter ses conseils à vos besoins uniques.
➡️ Une mise en conformité proactive avec DORA est essentielle pour éviter des sanctions et garantir la continuité de vos activités. Contactez un avocat pour un audit personnalisé.